Son yıllarda, membran ayırma teknolojisi, kanalizasyon arıtımında yeni teknolojilerden biri olarak geniş çapta incelenmekte ve uygulanmaktadır. Yer çekimiyle ayırma, pıhtılaşma, emülsiyon kırma, yağ emme ve sıyırma, biyolojik bozunma, flokülasyon adsorpsiyonu, iyon değiştirme ve diğer geleneksel ayırma işlemleri gibi diğer teknolojilerle karşılaştırıldığında bu teknolojinin birçok avantajı vardır. Güçlü seçicilik, düşük enerji tüketimi, geniş uygulama aralığı, çevre dostu, basit ekipman, kolay kullanım vb. Yağ-su ayırma membranı, malzemeye göre organik membran ve inorganik membrana ayrılabilir. Organik membranın bilimsel araştırma ve ticari alanlarda geniş bir uygulama alanı vardır. Organik membranla karşılaştırıldığında inorganik seramik membran, güçlü kimyasal ve termal stabiliteye, mükemmel kir direncine ve basınç direncine, kolay temizlenebilir, yüksek mekanik dayanıma ve uzun ömre sahiptir, bu nedenle su içinde yağ emülsiyon ayrımı için seramik membran kullanımı büyük bir öneme sahiptir. akım. Hidrofobik modifikasyon, seramik filmin yağa karşı ıslanabilirliğini artırabilir, yağ içinde su emülsiyonunun ayırma verimliliğini artırabilir ve seramik filmin kimyasal stabilitesini ve dayanıklılığını artırabilir.
Yağ içinde su (W/O) emülsiyon sisteminin şekli, suyun yağ içerisinde küçük damlacıklar halinde dağılmasıdır. Membran ayırma sırasında membran kirlenmesi, kullanım süresinin uzamasıyla birlikte geçirgenlik akısının ve tutma oranının azalmasına neden olur, bu da membranın hizmet ömrünü kısaltır ve membran ayırma teknolojisinin uygulanmasını sınırlar. Seramik membran yüzeyinin modifikasyonu, membranın spesifik seçiciliğini ve ayırma etkisini artırabilir, membran yüzeyi ile gereksiz besleme molekülleri arasındaki etkileşimi azaltabilir ve membran kirliliğini bir dereceye kadar azaltabilir. Bu nedenle, yağda su emülsiyonlarının ayrılmasında genellikle, yağ damlacıklarının geçmesine ve membran yüzeyinin hidrofobik ve lipofilik özelliklerini kullanarak su damlacıklarını yakalamasına izin veren ve yağ-su etkisini elde eden hidrofobik bir film seçilir. ayrılma.

Seramik membran yüzeyinin hidrofobik modifikasyonu
Seramik film yüzeyinin hidrofobik modifikasyonu genellikle hidrofobik malzemelerin birleştirilmesi veya yapıştırılması, daha düşük bir yüzey enerjisinin seçilmesi, uygun pürüzlülük ve yüzey yapısının seçilmesi (örneğin, yüzey kimyasal özelliklerini sağlamak için silan veya tiyol kullanılması ve mikron veya nanoyapının eklenmesiyle gerçekleştirilir). Daha iyi pürüzlü bir yüzey elde edin, film yüzeyinin hidrofobik etkisini geliştirin ve ayırma performansını artırın.
Seramik membran yüzeyinin hidrofobik modifikasyonu için üç yaygın yöntem vardır: emdirme, sol-jel ve kimyasal buhar biriktirme.
01. Daldırma yöntemi
Impregnation method (Impregnation method) does not require special equipment, just the original ceramic film directly immersed in hydrophobic substance solution, the method is simple and direct, easy to operate, low cost. The hydrophobic modification of ceramic membrane surface is carried out by immersion method, which usually uses the functional group of hydrophobic substance to connect with the hydroxyl group on the ceramic membrane surface through condensation reaction.
Taking siloxane as a modifier for example, the operation steps of the impregnation method are as follows: dissolve the organosilane in water or ethanol and hydrolyze it to obtain a reactive silanol solution; When the pre-treated ceramic membrane is immersed in the solution, the reactive silane molecules can be adsorbed on the surface of the membrane, and the hydrophobic membrane can be obtained.
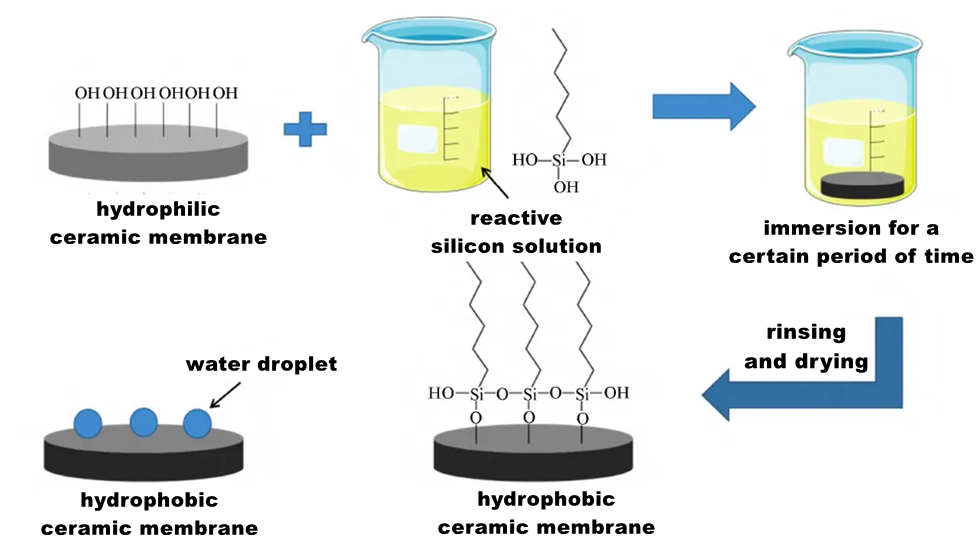
Hydrophobic effect is the result of the joint action of surface roughness and surface energy. In the study of hydrophobic modification of ceramic film, it is usually first to provide a certain rough micro-nano structure on the surface of ceramic film, and then modify it with low surface energy. In addition to the modification with silane coupling agent, mercaptan is also the preferred material to reduce the surface energy of the film.
In summary, the operation and steps of hydrophobic modification of the surface of ceramic film by impregnation method are relatively simple, and are greatly affected by the type of modifier, the concentration of modifier, the impregnation time, the number of impregnation times and the roughness of the surface of ceramic film. In addition, because the number of substances with low surface energy that react depends on its own concentration and the number of hydroxyl groups on the surface of ceramic film, Therefore, the method also has a great dependence on the reactive hydroxyl group on the surface of the ceramic membrane.
02. Sol-gel method
Sol-gel technique uses compounds containing highly chemically active components as precursors, and mixes these raw materials uniformly in the liquid phase. After chemical reactions such as hydrolysis and condensation, a stable transparent Sol system is formed in the solution. The sol is slowly polymerized among aged colloidal particles to form a gel with a three-dimensional network structure. The gel was dried and sintered to produce molecular and even nanostructured materials.
The hydrophobic modification of ceramic membrane by sol-gel method can form a large rough structure on the surface of the membrane, and can directly bind low surface energy chemicals. However, the early introduction of organosilane into the sol solution may lead to the formation of large volume polymers, resulting in poor modification effects.
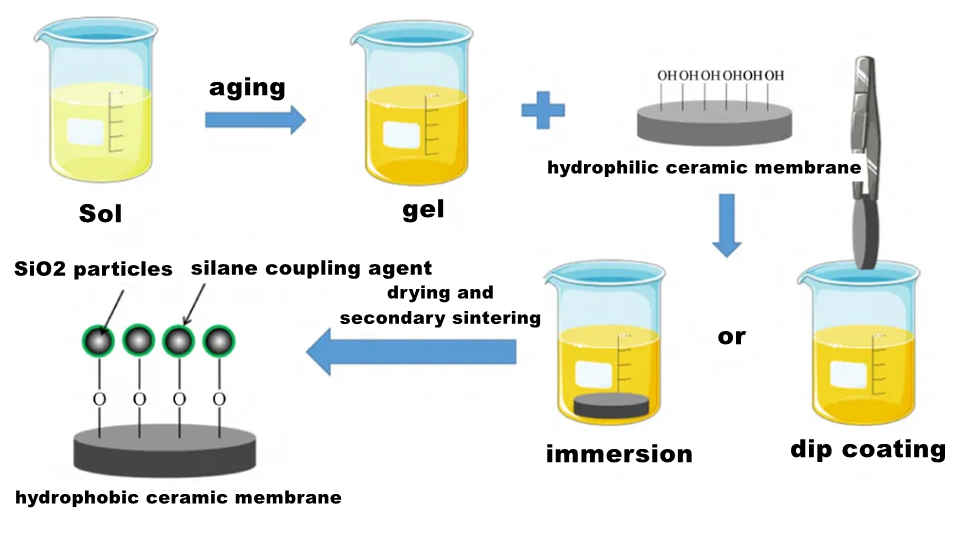
Compared with other methods, sol-gel method can prepare a stable hydrophobic surface with good separation effect, but it takes a long time to prepare the sol solution, and macromolecular polymers may be formed in the process, which affects the modification effect. In general, secondary sintering is required after the completion of coating, and the process is more complicated. In addition, excessive temperature during secondary sintering will destroy the structure of the film, reduce the hydrophobicity and stability of the film, and the aperture of the modified film will decrease with the increase of the number and time of sol-gel coating. In addition, the sol has an important effect on the formation of colloid in the process of colloid preparation, and then affects the film forming quality. Coating time and times, ambient temperature and humidity, heating rate, calcination temperature and calcination time all have a great influence on the subsequent coating drying process. At present, the process can be simplified by reducing the sintering steps at high temperature, forming a rough structure on the surface of the film at one time and combining with low surface energy materials, so as to reduce the damage of the film structure at high temperature.

03 Chemical vapor deposition method
chemical vapor deposition (CVD) uses gas phase reactants deposited on the substrate surface to form a solid film with specific chemical properties. The method has the advantages of controllable film composition, good film repeatability, uniform film layer, wide application range, no restriction on the shape of the substrate and no damage to the substrate material, and is an effective method to change the surface properties and microstructure of the film. For hydrophobic modification of the ceramic film using this method, the ceramic film needs to be placed in a closed container and heated at the boiling point temperature of the organosilane for a long time. The organosilane vapor is passed through to react with the hydroxyl group on the surface of the ceramic film, and the reaction principle is the same as that of the impregnation method.
Under normal circumstances, in order to make the organosilane reagent can be fully utilized, it is necessary to select a closed container with a size similar to the ceramic membrane, so that the contact and reaction of organosilane vapor with the ceramic membrane can be maximized.
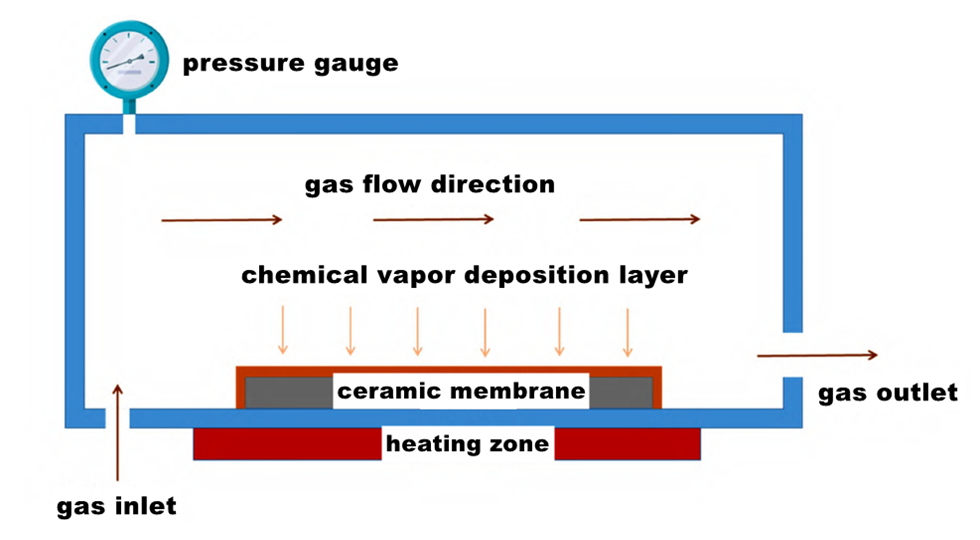
Kimyasal buhar biriktirme (CVD), filmin yüzeyinde mikro-nano parçacıklar ve nanoçubuklar hazırlamak ve düzenli mikro yapıyı oluşturmak için tercih edilen yöntemdir. Kimyasal buhar biriktirme ile modifiye edilmiş hidrofobik seramik film, düzgün film tabakası, iyi stabilite ve geniş uygulama aralığı avantajlarına sahiptir, ancak aynı zamanda hidrofobik film kalınlığı incedir, mekanik özellikler yetersizdir ve çatlaklar ve çatlaklar gibi kusurlar vardır. Dış etki altında kabarcıkların oluşması kolaydır. Su damlacıkları ve kirleticiler çatlaklardan filme nüfuz eder, iç yapısını bozar ve filmin hidrofobik özelliğini ve stabilitesini azaltır. Biriktirme reaksiyonunda yer alan bazı organosilanlar toksiktir ve insan vücuduna ve çevreye zarar verir. Ayrıca bu yöntemin gerektirdiği reaksiyon sıcaklığı yüksektir ve bunun sonucunda ortaya çıkan yüksek enerji tüketimi ve yüksek maliyet, gerçek endüstriyel üretimde uygulanmasını sınırlamaktadır.





























